The power of role-based e-learning: selected content, tables and figures
Chapter 6 Moderating online role play
- What Does “Moderating” Mean?
- Developing a Personal Style as a Moderator
- Modes of Learning – For Participants
- Modes of Action – For the Moderator
- Preparing for Success – Anticipating Problems
- Summary
Beyond the design space lies the terrain of the moderators. Their responsibility is to implement the design, make things happen and manage the consequences. An online role play without a moderator is unlikely to fulfil its learning objectives. This chapter introduces and explores the role of moderators – who may be the original designer, tutors working in a team-teaching context, or other educators selecting someone else’s design for use in their own context. It also locates the moderator role within the broader range of educational roles that may be more familiar to readers.
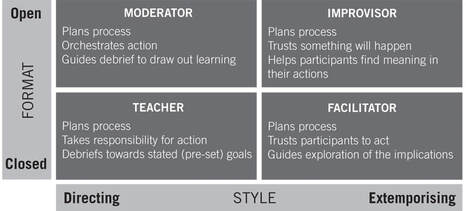
This can be an exciting and challenging role and the chapter provides insights into the processes of teaching and learning from that perspective. A moderator’s role is different to a teacher’s role and can involve as much learning for educators as for participants. It shares this, to some extent, with the requirements for implementing problem-based learning (see for example http://pbl.cqu.edu.au/).
Moderating an online role play can be very different from moderating a face-to-face role play in a classroom. For example, more attention may be needed to guiding learners’ written communications, because written messages can be more ambiguous than face-to-face exchanges where body language helps to convey a clear message. The chapter provides guidelines for educators wanting to understand what is involved in adapting current practices to extend their repertoire and expand capabilities.
Figure 6.2 Styles of moderating role-based e-learning
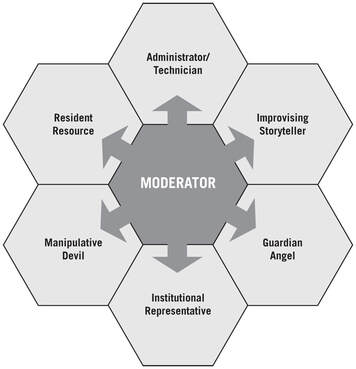
Figure 6.4 Six types of moderator roles in role-based e-learning
Table 6.4 Aligning the six moderator roles with the action phase and control factors in online role play
| Moderator roles | |
| File Size: | 34 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
Summary
The models and concepts discussed in this chapter offer useful perspectives on enacting the role of moderator. Developing capabilities as a moderator requires making allowance for the shifts in perspective when stepping into an unfamiliar role. Having a clear understanding of personal “mental models” about how to guide learning processes will ensure that a moderator is equipped to handle both routine and unexpected eventualities. Making available to participants one or several models to guide awareness of differing approaches to learning also enables them to more readily accept the task of directing their own learning.
This chapter focused on role play implementation in regard to interpersonal and intrapersonal capabilities for moderating online role play. The following chapter explores the platform options to support their implementation.